102 Silicate Lab, IIT Bombay,
Powai, Mumbai – 400076

Education:
M.Tech. (Chemical Engineering), Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India (2020)
B.Tech. (Chemical Engineering), Alagappa College of Technology Chennai, Anna University, India (2017)
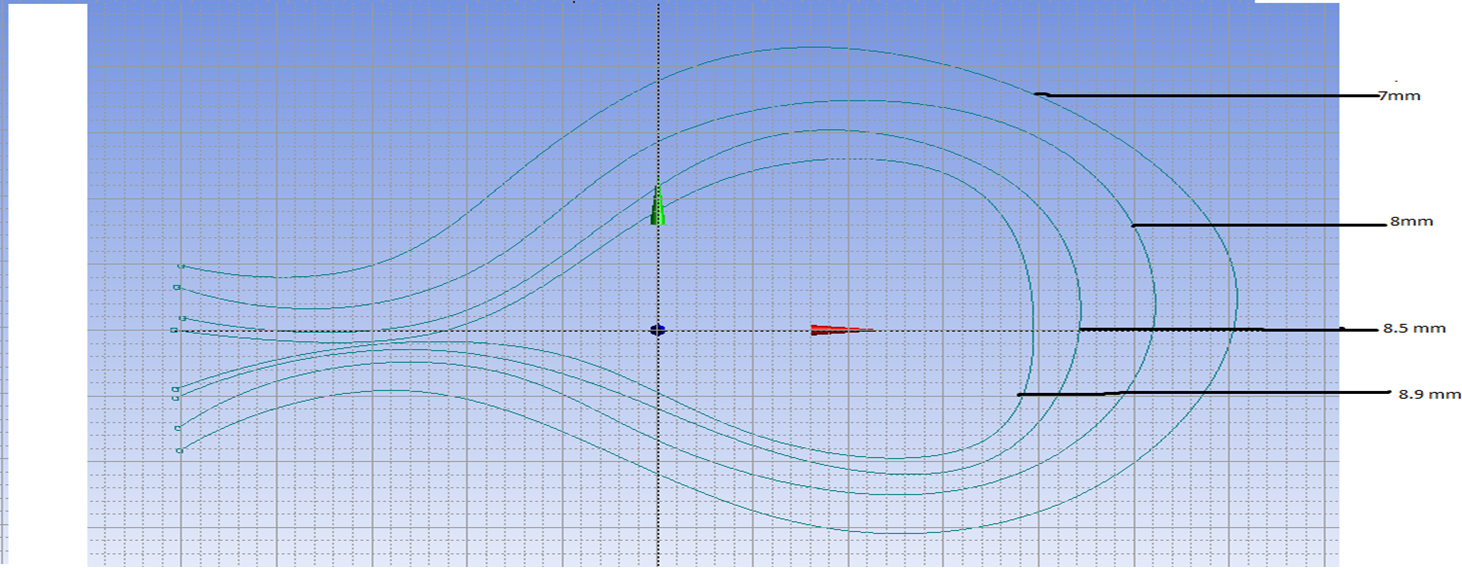
Thesis research topic: Design of occlusion device with bio-resorbable material for ASD defect by using Finite Element Analysis.
Research Summary:
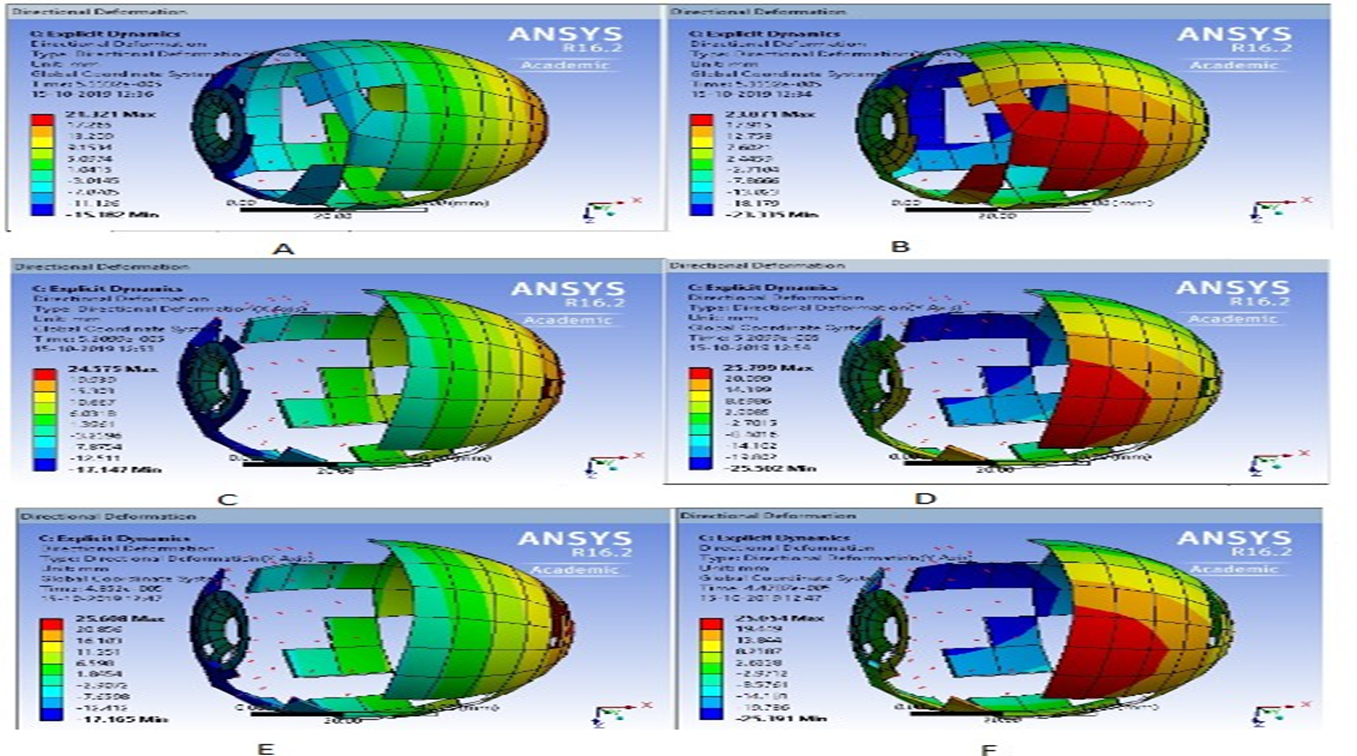
The occlusion devices are used to treat congenital heart defects such as Atrial Septal Defect (ASD), Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD), and Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA). The deployment of these devices causes effects to some patients such as embolization, tissue injury, proliferation, thrombosis. Eventually, the implanted patients need to be admitted in a hospital and immediate surgery to remove devices and then replaced with a new device. These problems are arises due to many reasons such as improper design, material incompatibility, friction between the device and blood vessel, wear upon the device, and tissue when both are in relative motion. The main objective of this project is to design the occlusion devices with optimal design by using the Finite Element Method. The design and tribology studies, the software ANSYS would be the best option. The tribology problem was studied with the help of a literature survey and finally stated the model for wear analysis as Archard’s wear equation. The balloon expansion and bursting were executed in the ANSYS by using tools of explicit dynamics. These results would be useful to study the deformation of the balloon with respect to the applied pressure into it.
Keywords: Atrial Septal Defect, Ventricular Septal Defect, Patent Ductus Arteriosus, Stainless steel, Nitinol, Dacron, Polyurethane, Chinese lantern design, ANSYS Explicit dynamics, balloon Bursting nominal pressure
Graphical representation of research work: