102 Silicate Lab, IIT Bombay,
Powai, Mumbai – 400076

Education:
Ph.D. Student (Chemical Engineering), Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India (2019-present)
M.Tech. (Chemical Engineering), Indian Institute of Technology Gandhinagar, India (2019)
B. Tech. (Chemical Engineering), Bipin Chandra Tripathi Kumaon Engineering College, Dwarahat, Uttarakhand, India (2016)
ORCID ID: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0306-1306
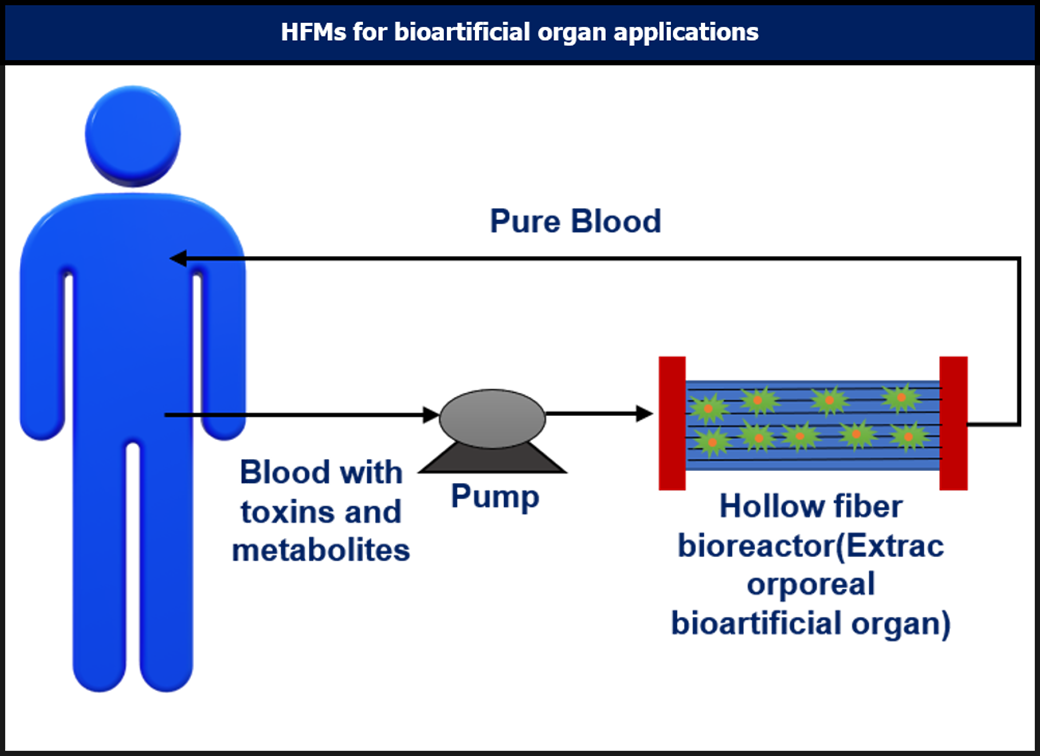
Thesis research topic: Hollow fiber membrane for bioartificial organ application
Millions of people worldwide are suffering from organ failure and hormone deficiency due to various reasons like accidents, lifestyle habits/ disease, senescence. The cure for this problem is partial or whole organ transplantation, but the scarce availability of donor, expenditure of the treatment process, and the risk in surgery limits this option. Therefore, a biological support system is required to mimic the function of organs and hormones in demand by the patients. My research focus is based on the development of Bioartificial organs which mimic the function of natural organs like kidney, liver, pancreas based on hollow fiber membranes (HFMs). Therefore, a correct grade of raw materials should be identified for the fabrication of HFMs in bioartificial organs, which makes them bioactive, biomimetic, and biocompatible. These biocompatible HFMs are used for the fabrication of dialyzers (lab-scale and full-scale) for hemodialysis (Artificial Kidney) application. Animal trails of the full-scale dialyzers are underway, and later clinical trials should be done to transfer our technology for public benefits. In addition to this, the development of a commercial scale extracorporeal device based on HFMs for bioartificial kidney and bioartificial liver applications. Also, the development of a device for the bioartificial pancreas to maintain controlled release of insulin inside the body of a diabetic patient.
Keywords: Hollow fiber membranes; bioartificial organs; biocompatibility; hemodialysis; extracorporeal device
Graphical representation of research work: