Prof. Sharad Bhartiya Research Group IIT Bombay
Automation Lab
Optimal operation of SMBC
- Details
Optimal operation of Simulated Moving Bed Chromatography (Sponsor: DST)
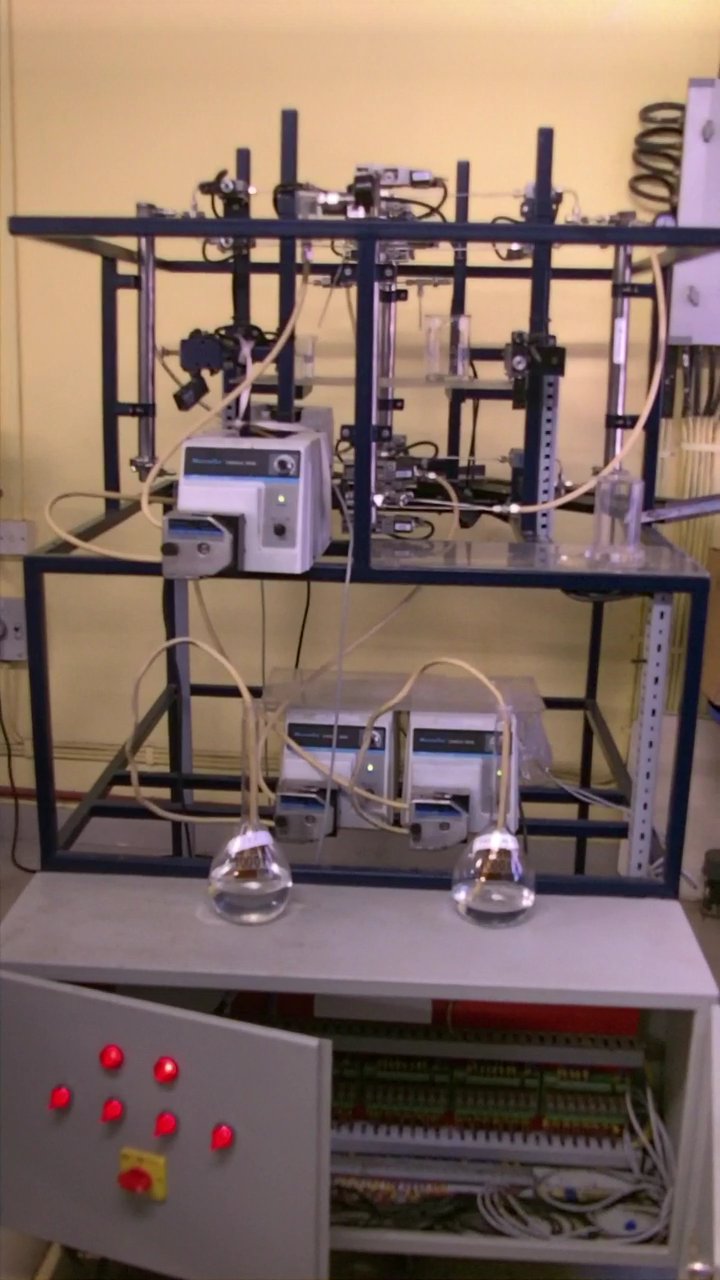

Simulated Moving Bed Chromatography (SMBC) is an adsorption based continuous separation process. The parex process for xylene separation is a popular example in the petrochemical industry. Similar applications are found in the pharmaceutical industry. SMBC is a technical realization of the counter current adsorption process approximated by sequentially switching the inlet and outlet valves of interconnected columns in the direction of fluid flow. Due to the switching nature, the process is dynamic in nature and only cyclic steady state operation can be achieved. In this work, we use dynamic optimization to obtain optimal transitions between optimal operating points.
In this work, systematic optimization study is carried out for different operational goals in SMBC to enhance the performance of an existing setup. The optimization work involves Pareto optimal solution for two different conflicting objective functions. Optimal transition between such operating conditions is a challenging task. This article proposes new optimal transition strategies which allow dynamic changes in operating conditions for better transition. The quantitative results obtained by comparing the optimal transition method with a non optimal step change method shows that the optimal transition requires less of time to achieve the new reference cyclic steady state. The new operating strategy (dual switching) is also explored which involves changing the operating variable periodically after every 2 switches. However, an optimization results suggest that the frequent changes in operating conditions are not able to change objective function much but increases product concentration as compared to single switching case. This is due to the high loading of fructose in columns as operating parameters are changing frequently. All of the above methods are applied on a SMBC process for separation of glucose and fructose using Ca++ exchange resign.